Contents:

microeconomics vs macroeconomics is significant in the case of price determination, demand, supply, labor cost, etc. Macro is substantial in the formulation of fiscal and monetary policies. Let us see the top differences between macroeconomics vs. microeconomics. It is not uncommon for people to interchangeably use microeconomics and macroeconomics. However, these two fields of study are distinct from each other and have different applications.
The term also considered taxes, regulations, and government legislation. It doesn’t try to explain which actions should take place in a market, but rather the effects of changes in certain conditions. Microeconomics has applications in trade, industrial organization and market structure, labor economics, public finance, and welfare economics. Macroeconomics developed as a discipline in its own right in the 1930s when it became apparent that classic economic theory was not always directly applicable to nationwide economic behavior. Classic economic theory assumes that economies always return to a state of equilibrium.
But, the housing market is so influential that it could also be considered a macro-economic variable, and will influence monetary policy. Macroeconomics account for the aggregate demand and supply of a nation’s economy. John Maynard Keynes, considered the founding father of macroeconomics, wrote The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money in 1936. In the book, he introduced the simultaneous consideration of equilibrium in goods, labor, and finance.
Microeconomics focuses on the analysis of how supply and demand determine prices and quantities of goods and services in the market. It also studies the effects of government policies on individual economic units and how they respond to changes in market conditions. Economics is broadly divided into two different categories namely microeconomics and macroeconomics.
It analyses how the macroeconomic conditions or factors affect the behavior of the market and the results of those. Overall, understanding microeconomics and macroeconomics is crucial in comprehending how the economy works and how various economic policies can affect individuals and society as a whole. Behavioral economics is a relatively new field that challenges the traditional assumptions of microeconomics and macroeconomics. Behavioral economists argue that individuals do not always act rationally and that their decisions are influenced by a variety of factors, including emotions and social norms. This can make it difficult to apply traditional economic principles in certain situations. For example, individuals may be more likely to make decisions based on their emotions rather than on rational economic considerations.
What is the difference between macroeconomics and finance?.
Posted: Sat, 25 Mar 2017 17:25:10 GMT [source]
Although there are some dissimilarities between Micro economics and Macro economics, both are important and need to be understood to get a comprehensive knowledge of economics. To understand the domestic economy is important but at the same time it is also important to understand the household economy and the economy as a whole as it helps to to set a nation’s economic policy. Microeconomics accounts for factors like the demand and supply of a particular commodity. Another feature of macroeconomics is that it focuses on aggregated growth and its economic correlation.
Aggregate demand is one of the key price determinants in markets as it offers insight into how much the entire market value a good or service. Keynesian EconomicsKeynesian Economics is a theory that relates the total spending with inflation and output in an economy. It suggests that increasing government expenditure and reducing taxes will result in increased market demand and pull up the economy out of depression. A higher price set by sellers would cause a surplus of stock (surplus/excess quantity supplied), forcing them to lower costs to match thecorrespondingdemand. Conversely, a lower price set by sellers would cause a shortage of stock , forcing prices to go up to keep pace with thecorrespondingdemand. This relationship between demand and supply attained the ‘state ofequilibrium‘ or the optimal relationship when the quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal.
Keynesian vs. Neo-Keynesian Economics: What’s the Difference?.
Posted: Sat, 25 Mar 2017 18:22:46 GMT [source]
The overall price level is determined by the interaction between aggregate supply and aggregate demand. For each of the following, determine whether the topic would be considered part of macroeconomics or microeconomics. Before the Great Depression, it was assumed that the macroeconomy also behaved in the same manner as the microeconomy.
If a good or service is scarce, chances are good that it’ll most likely attract greater demand. Similar to utility – if a product or service is very useful, more individuals will have a demand for it. Business CyclesThe business cycle refers to the alternating phases of economic growth and decline. Microeconomics resolves internal issues, while macroeconomic principles apply to the environment and eternal matters. Quantity DemandedQuantity demanded is the quantity of a particular commodity at a particular price.
It can help determine the causes of inflation, unemployment, and economic growth. Macroeconomics can also be used to study the effects of government policies, such as fiscal and monetary policies, on the overall economy. Economics is a complex field with many fixed factors and variables affecting the financial health of individuals, households, companies, and governments. A firm grasp of the principles and theories governing microeconomics and macroeconomics will help professionals make wise decisions concerning nearly all areas of business. Because microeconomics focuses on the behavior of small units of the economy, it tends to limit itself to specific and specialized areas of study. This includes the balance of supply and demand in individual markets, the behavior of individual consumers , workforce demand, and how individual companies determine wages for their workforces.
Microeconomics deals with the behavior of individuals and firms in making decisions regarding the allocation of resources. It focuses on the interactions between buyers and sellers in a specific market and how they determine prices and quantities. Microeconomics is useful in situations where the decision-making unit is small and the market is well-defined. Higher demand levels, personal income, etc. can influence price levels, which in turn can affect a nation’s economy. Contrarily, when supply outweighs demand, the cost of daily goods reduces. Microeconomics is the study of individual and business decisions regarding the allocation of resources and prices of goods and services.
Interest rates, as established by the Central bank and individual banks, can affect the stock market. Higher interest rates indicate that money has become more expensive to borrow. To repay for the increased interest costs, businesses would have to cut down on costs leading to laying off workers. Also, the company cannot borrow as much as it used to, adversely affecting its earnings. If house prices rise, this is a micro economic effect for the housing market.
Similarly, government subsidies can distort market outcomes by providing incentives for firms to produce more of a particular good or service than would be produced in a free market. One of the most common mistakes is using macroeconomics and microeconomics interchangeably. Microeconomics deals with the study of individual behavior and decision-making, while macroeconomics deals with the study of the economy as a whole. It is essential to understand the differences between the two fields to avoid confusion. Macroeconomics examines economy-wide phenomena such as gross domestic product and how it is affected by changes in unemployment, national income, rates of growth, and price levels. Microeconomics studies individual factors, and macroeconomics studies aggregate factors, but both focus on allocating limited resources.
So, a region is considered in better health when the ratio of GDP to expenses is higher, meaning in lay terms that a nation is bringing in more than it puts out. Another measure used is GDP per capita, which is a measurement of the value of all goods and services divided by the number of participants in an economy. For example, the U.S. and China have a similar overall GDP, but the U.S. has a far better GDP per capita due to its far fewer economic participants, reflecting the higher standard of living in the U.S. Macroeconomics is also used to develop strategies for economic improvement at the nationwide and global levels. International trade is defined as the exchange of goods and services between countries. Global trade allows a country to focus on exporting products or services it can provide more efficiently than other countries.
Microeconomics and macroeconomics are two branches of economics that are essential in understanding how the economy works. In summary, microeconomics focuses on individual economic agents such as households and firms, while macroeconomics studies the economy as a whole. While there are differential lines between microeconomics and macroeconomics, they are interdependent to a large extent. Inflation and its implications for the cost of living are a common focus of investigation in the study of macroeconomics. However, since inflation raises the prices of services and commodities, it can also have acute implications for individual households and companies. Companies may be compelled to raise prices to respond to the increasing amounts that they have to pay for materials and the inflated wages they have to pay to their employees.
As the name suggests, Microeconomics studies the decisions made by individuals and businesses concerning the distribution of resources and prices of goods and services. It deals with a specific industry or a sector, the connections of firms and households in the market. At the same time, saying so, we also consider the taxes and other regulations that governments have created. It primarily focuses on the supply, demand, and other forces that define the price levels of goods and services in the economy.
Macroeconomics studies an overall economy or market system, its behaviors, the factors that drive it, and how to improve its performance. The indirect effect is based on supply and demand for the underlying company’s products and services. If the company’s products are flying off the shelves because of robust demand, it may be on a probable strong earnings trajectory that would likely translate into a higher price for its stock. But if demand is sluggish and there is excess inventory of its products, the company’s earnings may disappoint and the stock may slump.
Therefore, all other factors remain the same, the quantity supplied increases as the price increases, and the quantity supplied decreases . MicroeconomicsMicroeconomics is a ‘bottom-up’ approach where patterns from everyday life are pieced together to correlate demand and supply. Factors Of ProductionFactors of production define resources used to produce or create finished goods and services, the sale and purchase of which keeps the market economy afloat.
Utility is the measure of how useful a resource is to a decision-maker. Macroeconomics is the study of the decisions of countries and governments. The term analyzes entire industries and economics rather than individuals or specific companies.
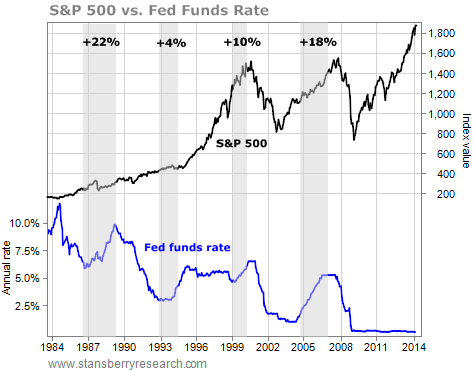
International finance is defined as the study of monetary interactions between two or more countries. The first concept, the Mundell-Fleming model, is defined as the interaction between the goods market and the money market, based on the assumption that the price levels of goods are fixed. Both microeconomics and macroeconomics involve examining economic behavior, but they differ in terms of the scale of the subjects being studied. For most macroeconomists, the purpose of this discipline is to maximize national income and provide national economic growth.
Microeconomics also focuses on issues arising due to price variation and income levels. A macroeconomic factor is an economic, environmental, or geopolitical event that broadly affects a regional or national economy. Keynesian economics comprise a theory of total spending in the economy and its effects on output and inflation, as developed by John Maynard Keynes.
Macroeconomics looks at the overall performance of the economy, including factors such as inflation, unemployment, and GDP. When a business decides to expand into a new market, it is making a microeconomic decision based on its own growth strategy. Microeconomics can help individuals make decisions about how to allocate their time and resources. Macroeconomics provides insight into how government policies affect the economy. Inflation signifies a rise in the general level of prices over one year. When inflation is low, the stock market reacts with a rush to sell shares.
SMiLE 整骨院
| 診療時間 | 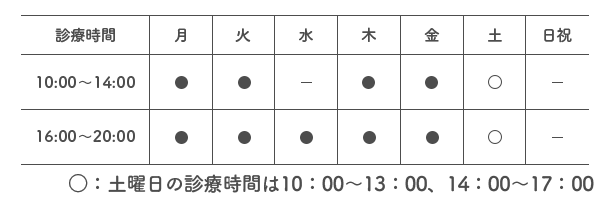 |
|---|---|
| 住所 | 〒112-0006 東京都文京区小日向4-5-10 小日向サニーハイツ201 |
| アクセス | 東京メトロ丸の内線「茗荷谷」駅 徒歩2分 |