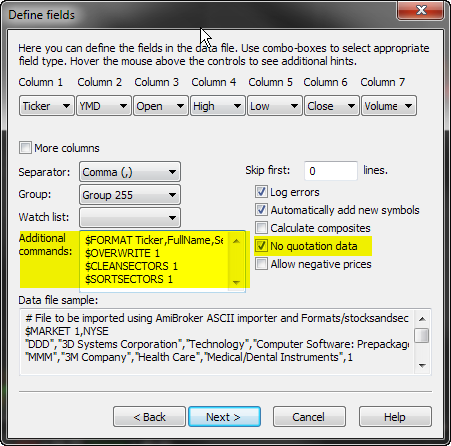
Content
However, this method can distort your income and expenses, especially if you extend credit to your customers, if you buy on credit from your suppliers, or you keep an inventory of the products you sell. If the budgeted number of units differs from actual production, both material cost and labor cost are impacted. For this example, assume that the number of gloves actually produced matches the budget. Outfield incurs labor costs to run machinery, and to package completed gloves for shipment to customers. The labor hours required per glove, and the labor rate determine the direct labor costs. The budgeted labor cost is $25 per hour, and each glove requires two hours of labor.
A word that means to add a column of numbers as in "Foot the amounts listed in column A." Also see crossfoot.
We explain and illustrate with an interactive model the use of forward-priced multiples in DCF. We also discuss the choice of multiple (including why EV/EBITDA may not be the best) and whether to apply the exit multiple to reported or adjusted profit. All ‘earnings-before’ measures create comparability issues, omit key components of operating performance, and what does foot mean in accounting should be interpreted with caution. We think EBITDA-AL is worse than EBITDA, which never was that useful in the first place. Better to use EBIT, EBITA or EBITDA-AMCE, where maintenance capital expenditure replaces D&A. The time from presentation to diagnosis was 8 weeks, and from diagnosis to death was 4½ months—neither of which is unusual in this setting.
The two footings are netted together to calculate the account balance for the period. The account balance is the amount that’s carried over to the financial statements. The term “footing” is appropriate because the totals are located at the end of each column. Footings are commonly used in accounting to determine the final account balances, which are reported on a company’s financial statements. Variance Analysis Variance analysis is a method for companies to compare its actual performance vs its budgeted amount for that cost measurement . The differences between the standard amount of cost and the actual amount that the organization incurs is referred to as a variance.

This practice has made analysing the performance of insurance companies extremely difficult for investors. The treasury stock method for calculating diluted earnings per share only considers the intrinsic value of written equity options, such as warrants and employee stock options. We explain why this is a problem and the further reasons why the full economic value dilution resulting from these securities is not reflected in financial statements. The friend had suggested that he might benefit from a below-knee walking cast, which was subsequently applied on the supposition that this was an occult fracture. Although he concurred with the probable diagnosis of stress fracture, he suggested measuring the patient’s C-reactive protein level and erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The results of both tests came back a week later and revealed an elevated level of 415.3 nmol/L (normal range 0.0 to 76.2 nmol/L) and rate of 35 mm/h (normal range 0 to 14 mm/h), respectively.
As discussed in LG 2.3.2, the period of use could be consecutive or nonconsecutive periods of time. A customer would not control an asset if another party has the right to more than an insignificant portion of the potential economic benefits. This is not a probability analysis as to who is likely to receive the benefits; the assessment should focus on the contractual rights of the respective parties. Specifically, the rights to the output and other economics derived from use of the asset should be considered. If a customer does not have contractual rights to all of the existing capacity of the asset, and the arrangement does not grant the customer an option to acquire any additional capacity, the arrangement is unlikely to be a lease. However, if the customer has the option to increase the volume of the output it consumes before it is given to additional customers , the arrangement likely meets this criterion.
Under either scenario, the customer will generally be deemed to have the right to direct the use of the asset if, during the period of use, the customer may operate the asset, or may direct others do so without the supplier having the right to change that right. Operating an asset takes different forms depending on the nature of the asset. Determining whether a customer operates an asset may be straightforward when an asset requires active operations (e.g., construction equipment). Other assets require little active operation (e.g., storage containers) or are completely automated (e.g., a solar panel); and it may be more difficult to determine whether a customer operates such asset. However, a customer’s right to turn an asset on or off, to disconnect an asset from other assets, or to “pull the plug” would generally be considered a right to operate the asset.
In contrast, costor managerial accounting is intended to aid internal managers in their responsibilities of planning, monitoring and control. The IR&D and B&P project costs shall consist of all allocable costs, except business unit general and administrative expenses. Other methods for calculating the cost of money to be capitalized, such as the method used for financial accounting and reporting, may be used, provided the resulting amount does not differ materially from the amount calculated by use of paragraphs and of this subsection.
Compensated personal absence means any absence from work for reasons such as illness, vacation, holidays, jury duty or military training, or personal activities, for which an employer pays compensation directly to an employee in accordance with a plan or custom of the employer. Material-quantity standard means a pre-established measure, expressed in physical terms, of the quantity of material. By description of any other estimating technique employed to provide appropriate recognition of any unallowable costs pertinent to the estimates. The percentage of the segment’s operating revenue to the total operating revenue of all segments. For this purpose, the operating revenue of any segment shall include amounts charged to other segments and shall be reduced by amounts charged by other segments for purchases.
Additional benefits such as permanent and total disability and death payments, and survivorship payments to beneficiaries of deceased employees may be an integral part of a pension plan. The fair market value of the assets held by the funding agency as of a specified date is the Funding Agency Balance as of that date. Contractor “A” has one contract which requires two custom-ordered, high-value, airborne cameras. The contractor’s established policy is to order such special items specifically identified to a contract as the need arises and to charge them directly to the contract. Another contract is received which requires three more of these cameras, which the contractor purchases at a unit cost which differs from the unit cost of the first two cameras ordered.

SMiLE 整骨院
| 診療時間 | 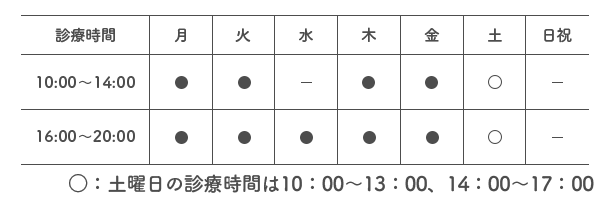 |
|---|---|
| 住所 | 〒112-0006 東京都文京区小日向4-5-10 小日向サニーハイツ201 |
| アクセス | 東京メトロ丸の内線「茗荷谷」駅 徒歩2分 |